Dry Transformer and Oil Immersed Transformer Manufacturer
News
Understanding Step-up and Step-down Transformers
Transformers are essential electrical devices used in various applications to transfer electrical energy efficiently. Among the different types of transformers, step-up and step-down transformers play crucial roles in adjusting voltage levels in electrical circuits. This article delves into the functions, working principles, applications, and differences between step-up and step-down transformers.
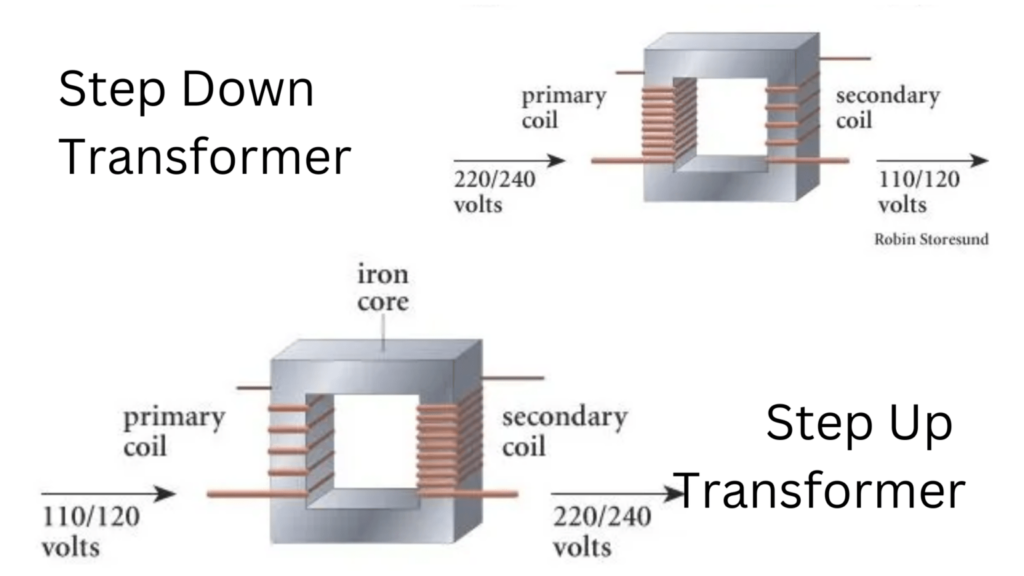
Fundamentals of Transformers
Transformers are electromagnetic devices that transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another through electromagnetic induction. They consist of primary and secondary coils wound around a common core, usually made of iron. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary coil, it generates a changing magnetic field, inducing a voltage in the secondary coil. This process allows for the transfer of energy without direct electrical connection between the two circuits.
Step-up Transformers: Increasing Voltage Levels
A step-up transformer is designed to increase the voltage of an electrical circuit. This is achieved by having more turns on the secondary coil compared to the primary coil. As the AC current passes through the primary coil, it creates a magnetic field that induces a higher voltage in the secondary coil due to the increased number of turns. Step-up transformers are commonly used in power transmission and distribution systems to raise voltage levels for long-distance transmission, reducing energy losses.
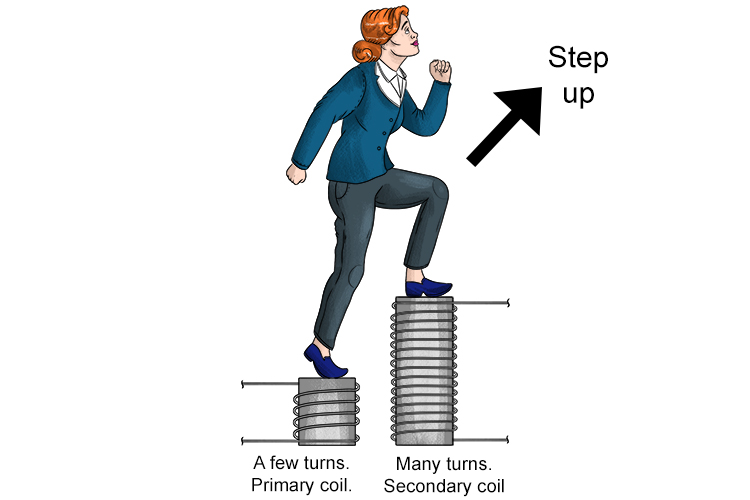
Why would you need a step-up transformer?
- To reduce power loss over long distances. By increasing the voltage, less current is required to transmit the same amount of power. This means less energy is lost as heat during transmission.
- To be compatible with equipment that requires higher voltage to operate. Things like industrial equipment, electric furnaces, etc., may need 200V, 480V or higher to run properly. A step-up transformer takes the voltage to the required level.
- For more efficient power distribution. It’s easier to transmit power at high voltages and then step it down for end use. So utility companies will use step-up transformersto raise the voltage for transmission via power lines, then step it back down for homes and businesses.
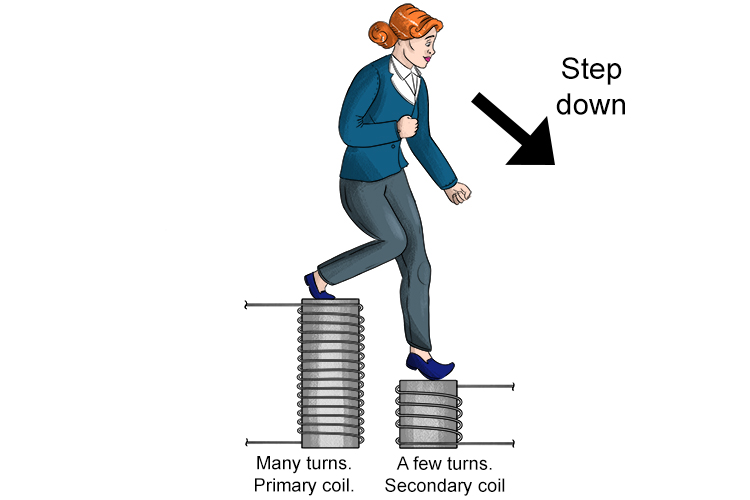
Step-down Transformers: Decreasing Voltage Levels
Conversely, a step-down transformer is designed to decrease the voltage of an electrical circuit. This is achieved by having fewer turns on the secondary coil compared to the primary coil. When the AC current flows through the primary coil, it induces a lower voltage in the secondary coil due to the reduced number of turns. Step-down transformers are widely used in household appliances, electronic devices, and industrial equipment to provide safe operating voltages for various applications.
Working Principles of Step-up and Step-down
Transformers The working principles of step-up and step-down transformers are based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction. When an AC current flows through the primary coil, it creates a changing magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary coil. The ratio of the number of turns in the primary coil to the number of turns in the secondary coil determines the voltage transformation ratio of the transformer. Step-up transformers have a higher secondary voltage compared to the primary voltage, while step-down transformers have a lower secondary voltage.
Choosing Between a Step-Up or Step-Down Transformer
A step-up transformer is used when you have a power source with a lower voltage that needs to be increased to a higher voltage. For example, if you have a 120V power source but need 240V to power certain equipment, you’d use a step-up transformer to boost the voltage. Step-up transformers are commonly used when connecting low-voltage circuits to high-voltage transmission lines.
On the other hand, a step-down transformer reduces the voltage from a higher level to a lower one. This is useful when powering low-voltage devices like electronics. For instance, the utility company provides power at a higher voltage, which is then stepped down to the standard 120V for residential use. Step-down transformers are also used for applications where a lower voltage is safer, such as powering landscape lighting, toys or other consumer goods.
Here are a few other things to keep in mind when choosing a transformer:
Power rating – Make sure the transformer can handle the amount of power you need. Higher power transformers tend to be larger and more expensive.
- Number of windings – Transformers typically have two windings, a primary winding and a secondary winding. But some have multiple secondaries to provide different voltage outputs.
- Efficiency – Look for “energy efficient” or low-loss transformers that minimise wasted energy released as heat. More efficient transformers tend to cost a bit more upfront but can save money in the long run.
- Indoor vs outdoor – Choose an outdoor, weather-resistant transformer for outdoor applications. Indoor transformers should only be used inside.
- Cost – In general, step-up transformers tend to cost slightly more than step-down transformers. Prices vary depending on the power rating and quality.
Step-up and step-down transformers are essential components in electrical systems for adjusting voltage levels to meet specific requirements. Understanding the functions, working principles, and applications of these transformers is crucial for efficient energy transfer and safe operation of electrical circuits. By utilizing step-up and step-down transformers effectively, engineers and technicians can optimize power distribution, enhance energy efficiency, and ensure reliable performance in various electrical applications.
Main Product
Contact Us
- Sales Manager: Eric
- Phone: +86-15515007426
- Whatsapp: +86-15515007426
- Email: info@byttransformer.com
Featured Product






